链表学习
约 3491 字大约 12 分钟
数据结构
2025-03-04
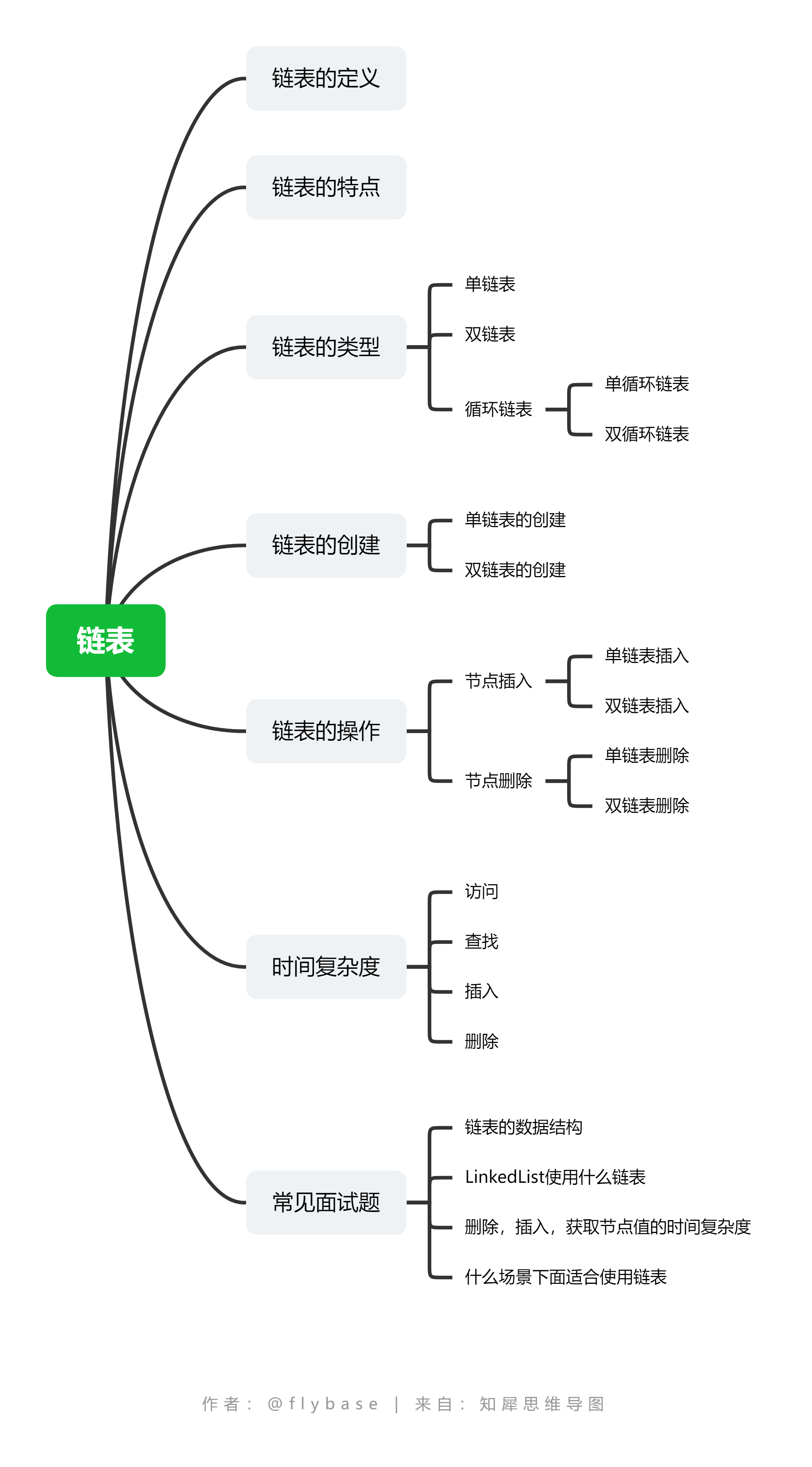
什么是链表
链表是通过指针串联在一起的一种线性结构,每一个节点有两部分组成,第一部分是数据域(存放对应的数据),第二部分是指针域(指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针指向空指针。
如图所示:
链表的特点
我们需要明确一点,那就是链表里面不是连续分布的,链表是通过指针来连接内存中的各个节点,那么就意味着不能和数组一样通过指定的下标来访问对应元素,只能通过指针遍历访问。但是链表不需要像数组一样需要预先申请空间,但是因为指针的存在,所以会占据部分空间。
链表的类型
有单链表,双链表,循环链表。
单链表

如上图所示,每一个节点都有一个数据域和指针域,指针指向下一个节点,通过指针的移动可以指向下一个节点。查询元素只能从前到后依次查询。
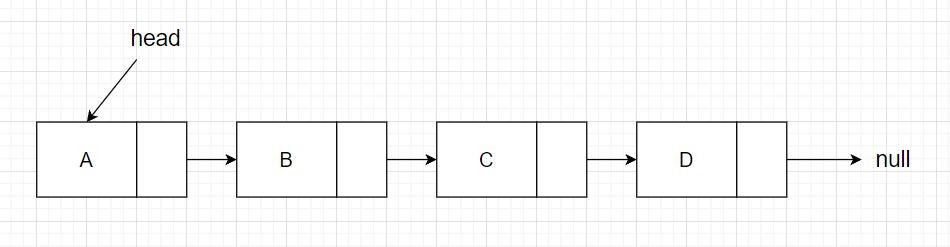
双链表
如上图所示,双链表里面有两个指针域,一个指针指向前一个节点,另一个指针指向后一个节点。双链表可以从前查询也可以从后查询,功能相对于单链表增加了。
循环链表
顾名思义,就是将链表的首尾相连接起来。
包含单循环链表和双循环链表。
下图展示单循环链表。
链表的创建(Java)
单链表
从以上介绍我们可以知道链表需要一个存储的值value,和移动的指针next。
public class Node {
// 数据值
int value;
// 指针
Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
// 无参构造
public Node() {
}
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}双链表
双链表相对于单链表,多了一个指向前面节点的指针prev。
public class Node {
// 数据值
int value;
// 后指针
Node next;
// 前指针
Node prev;
public Node(int value, Node next,Node prev) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Node() {
}
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}遍历链表
对于单链表,遍历只能从头节点开始一直到尾节点获取到对应的长度,双向链表也是一样。
public static int getListLength(Node head) {
int len = 0;
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
len++;
node = node.next;
}
return len;
}上面代码是定义了一个临时节点,让这个临时节点指向头节点,然后向后遍历,这样做的主要是为了不影响到头节点的位置,一旦头节点的位置改变了,那么之后无法获取到正确的头节点的位置。
插入元素
以下链表都默认为元素是递增的情况,否则部分情况不是太好操作的。
单链表
首先我们需要明确插入元素的位置,有首部,中部,尾部。
首部
插入在头部看起来简单,但是容易出错,总共有两步,第一步是先插入元素头头节点,第二步是插入元素之后,头节点就需要改成新的节点,不再是之前的节点了。
假设现在有链表 2>3->4需要插入1到头节点。
如下图所示
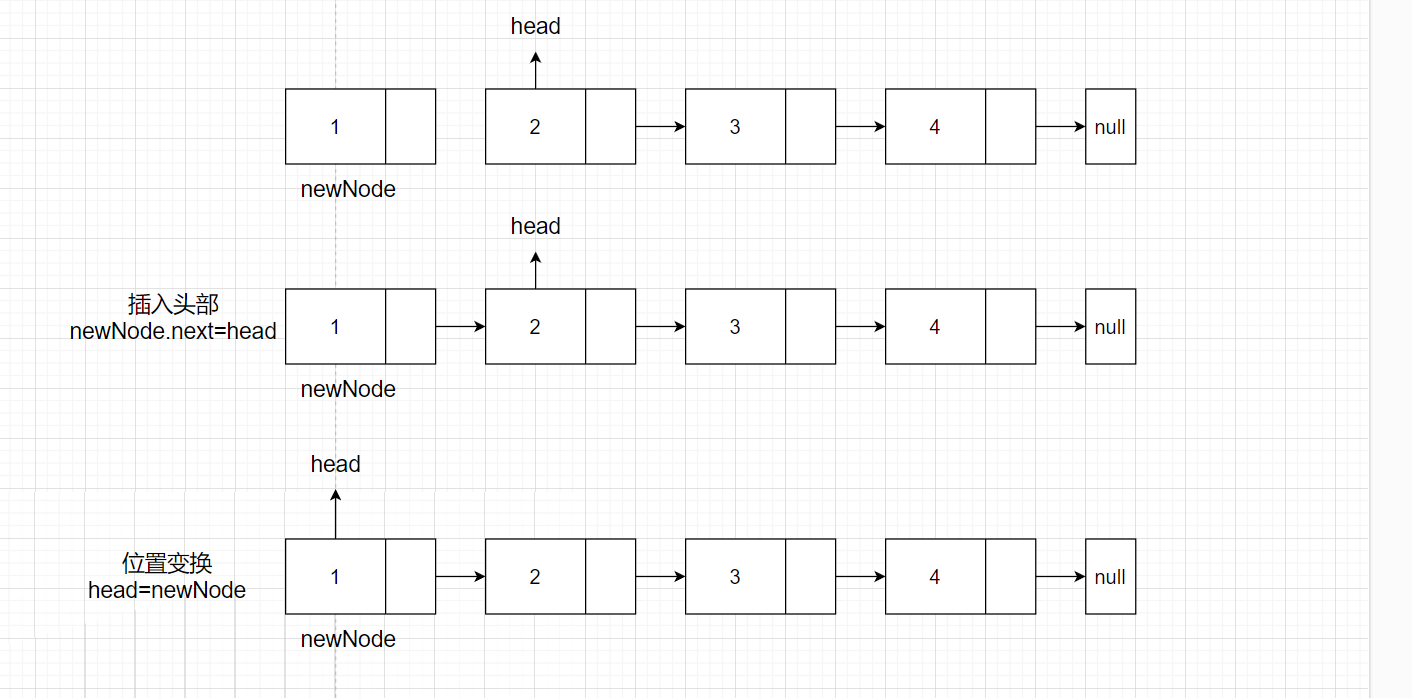
代码
newNode.next = head
head = newNode中部
假设现在我们有链表 1->2->4->null,现在需要插入元素3到第三个节点的位置,(如下图所示),首先我们需要遍历找到插入元素的位置,但是当我们找到第三个节点位置的时候,我们已经无法获取之前的节点元素,所以我们只能获取目标节点的前一个节点。
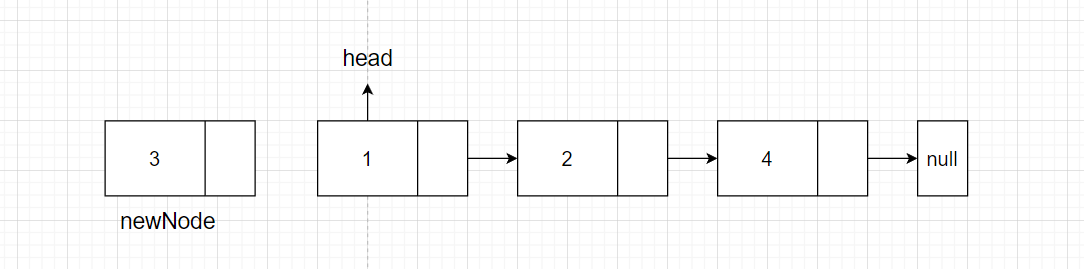
步骤如下
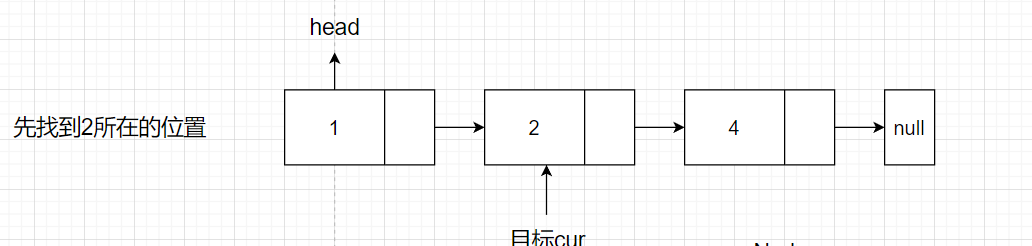
- 先找到2节点所在元素的位置
- 将newNode的下一个指针指向2节点的下一个节点的位置
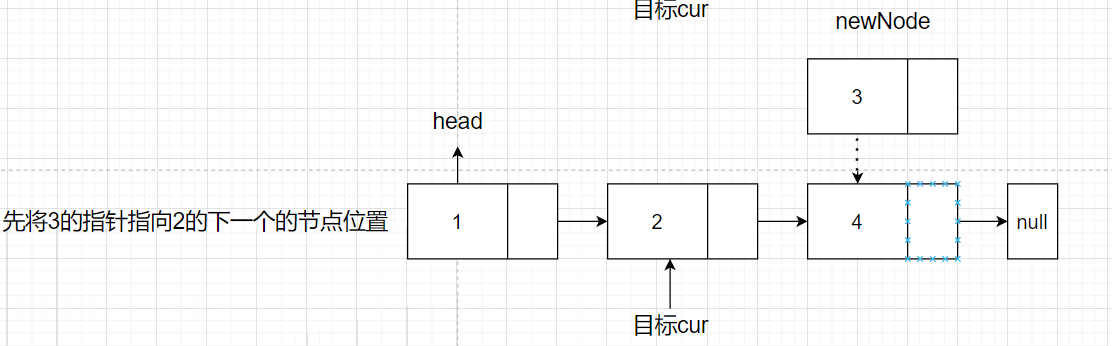
- 将2节点的指针指向newNode节点。
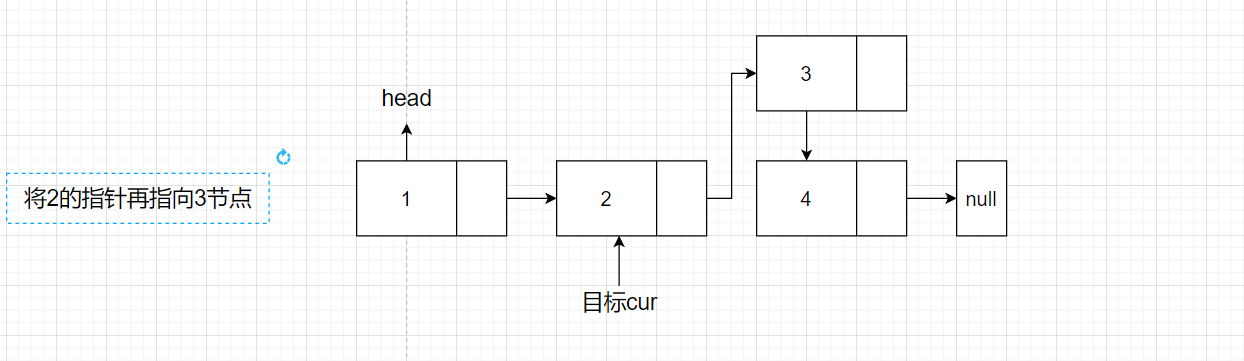
伪代码如下
Node cur = head;
int count =1;
找到前一个节点的元素位置
while(count < len -1){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
newNode.next = cur;
cur.next = newNode;注意第二步和第三步不能反过来,如果反过来了,那么cur先指向了newNode,它会自动断开与后续节点的关联,那么就丢失了后续的节点,无法连接。
尾部
尾部就相对简单了,只需要遍历到最后一个节点,将节点的下一个指针指向插入的元素就可以了。
总结
考虑到以上的三种情况,这边我们可以编写一个通用的方法来处理这些问题,而不是单独处理。
需要传递参数:头节点head,新的节点newNode,插入元素的位置position
步骤如下:
- 先判断头节点是否为空,为空只需要返回新的节点,这就是新的链表
- 头节点不为空,遍历获取链表长度,判断插入元素的位置是否再链表长度范围内
- 不在范围内,就意味着位置不合理
- 在范围内,判断是否是头节点的位置,是头节点的位置,就是头插法
- 不是头节点的位置,就是中部和尾部的插入方法,但是之前已经控制了范围,所以不需要判断尾部插入了,直接合并
- 返回新的头节点的位置
/**
* 插入指定位置的节点
* @param head 头节点
* @param newNode 插入节点
* @param position 插入位置
* @return 头节点
*/
public static Node insertNode(Node head, Node newNode, int position) {
// 1. 链表无元素
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
// 2. 获取链表长度
int length = getListLength(head);
// 3. 判断插入位置
if (position < 1 || position > length + 1) {
System.out.println("元素插入位置不合理");
return head;
}
//4.头插法
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
//5. 其余插入方式
Node temp = head;
int count = 1;
// 当temp指向position-1位置
while (count < position - 1) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}双链表
算法的话,单链表是比较常见的,双链表处理方法也是类似,Java里面的LinkedList就是典型的双链表的应用,后续将会结合使用。
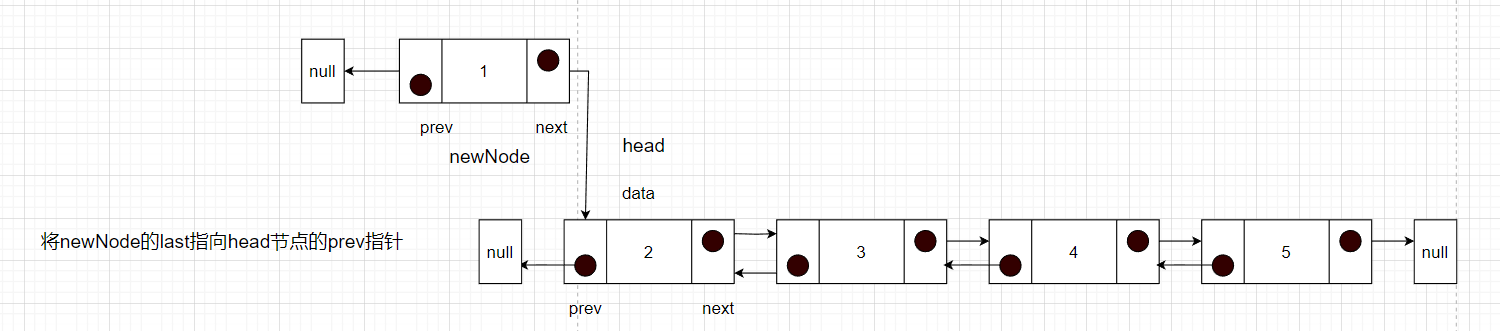
头插法
现在有2,3,4,5元素的双链表,希望使用头插法实现
步骤:
- 先记录头节点,设置新的节点的prev指针指向null
- 然后将新的节点的next指针指向头节点
- 然后将头节点的prev指针指向新的节点
- 确定新的头节点
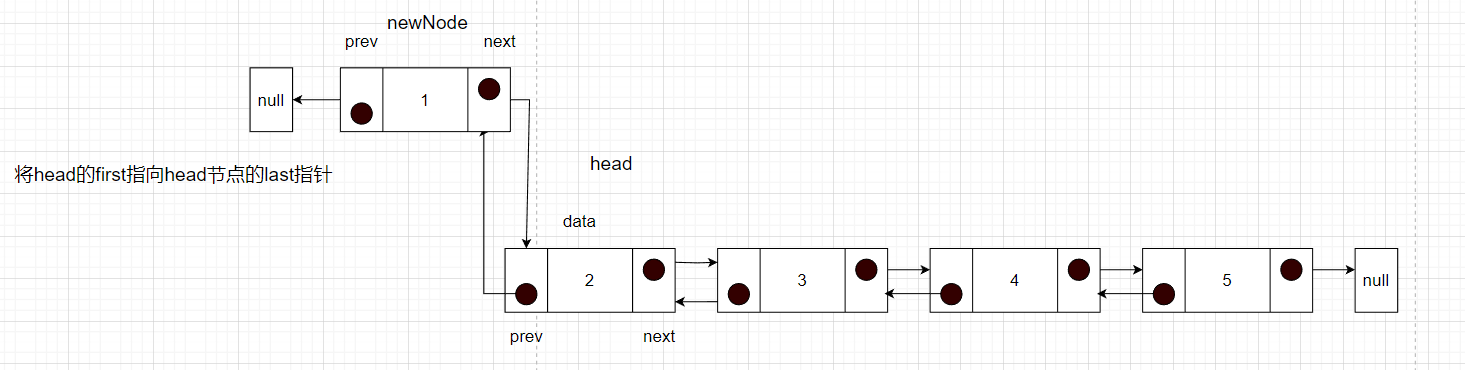
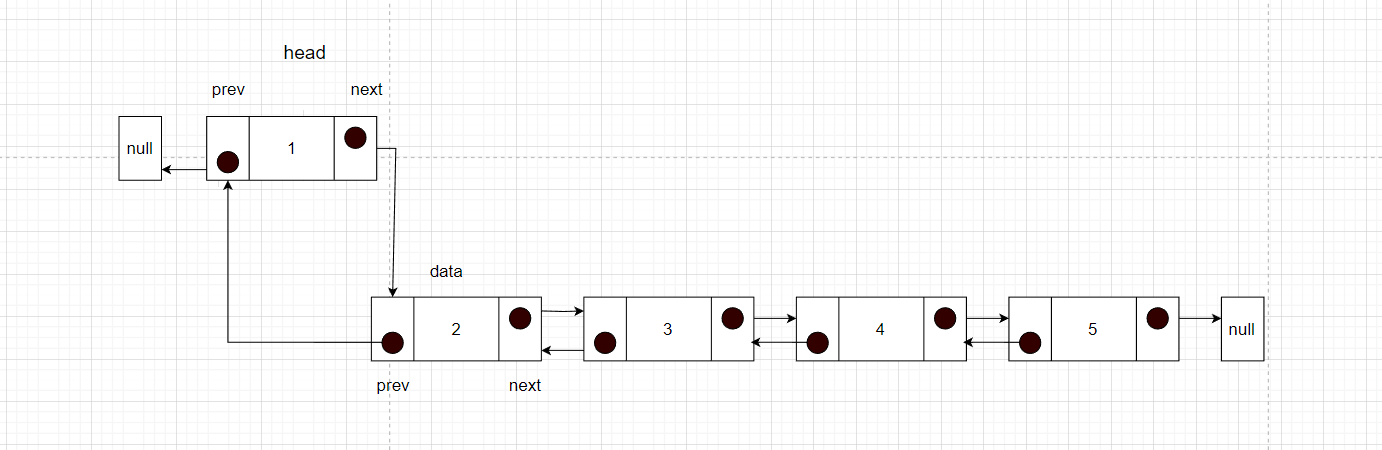
public static Node insertHead(Node head, Node newNode) {
newNode.prev = null;
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
return head;
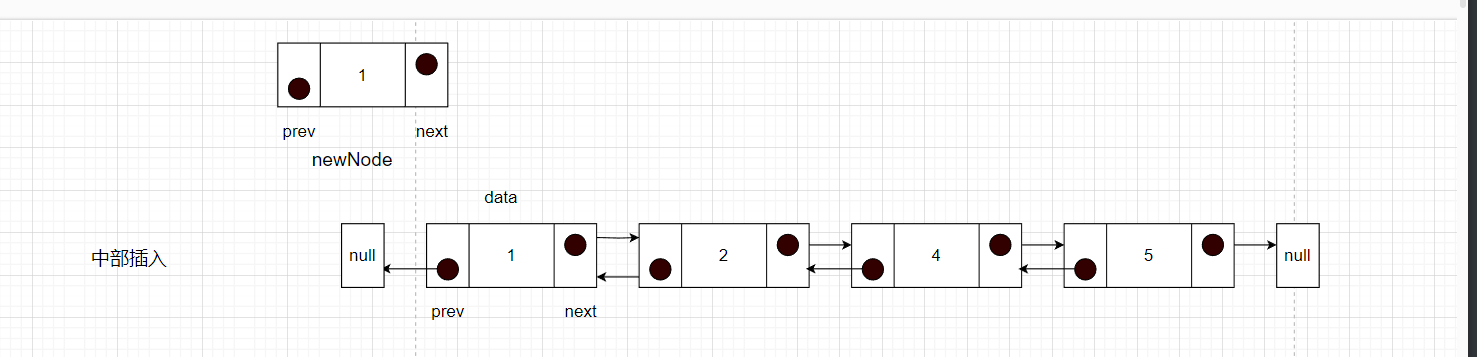
}中部
如下图所示
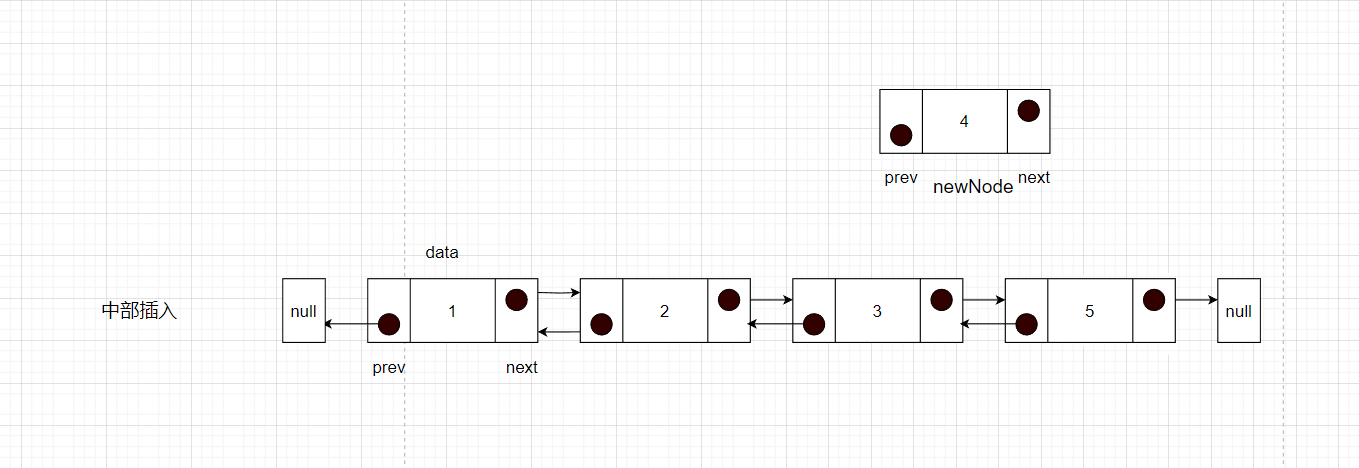
步骤如下
- 先要找到要插入元素的位置的前一个节点的位置,记为cur
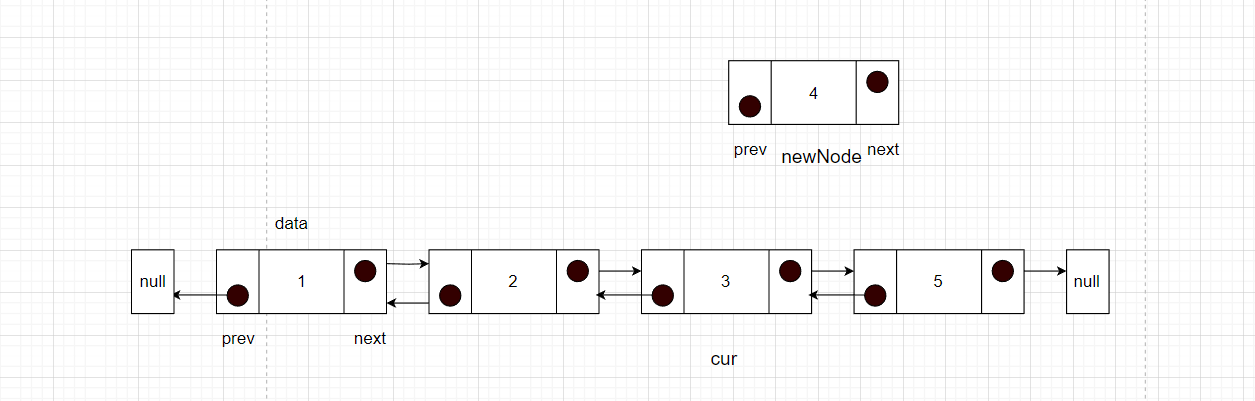
- 然后将newNode的next指针指向cur的next,就记录到了后面节点。
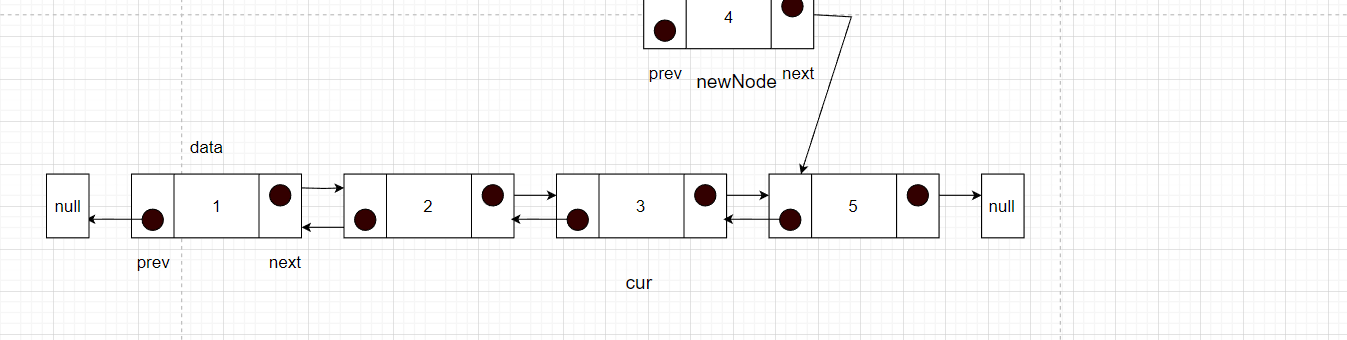
- 此时需要断开cur的下一个节点的prev指针,指向newNode,这样就将newNode和之后的节点绑定
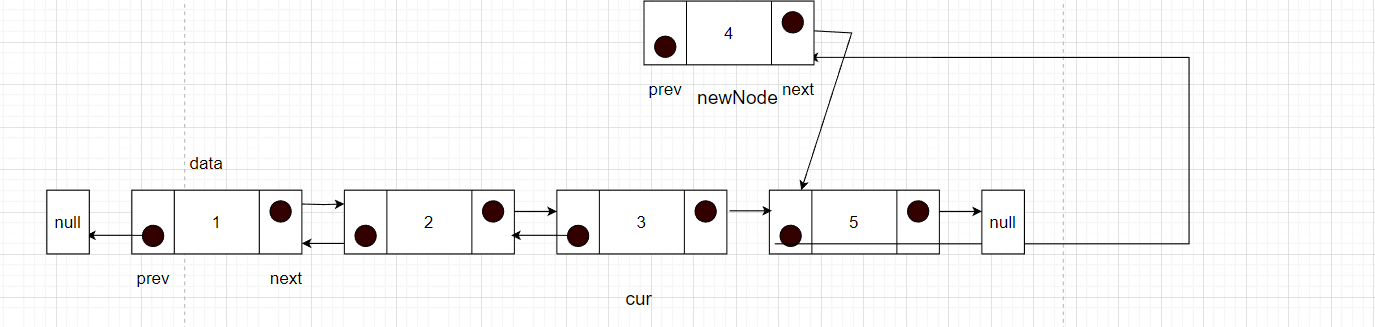
- newNode的prev指针就需要指向cur,开始和cur建立联系
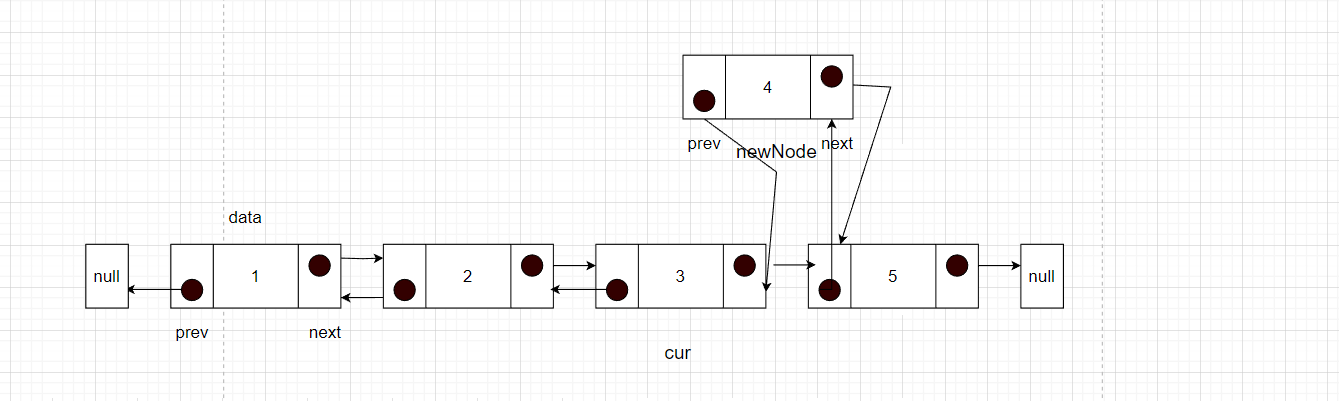
- cur的next指向newNode,完成插入
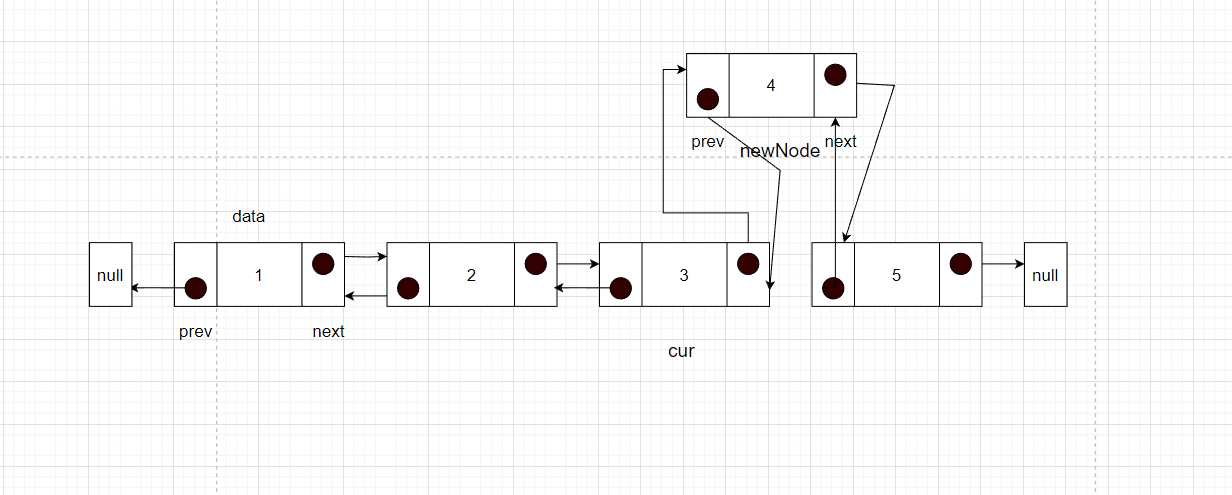
这里和单链表一样的问题,首先需要先将目标节点之后的这些节点和新节点建立联系,然后才是和目标节点建立联系,不能反过来,反过来了就丢失了后续的节点。
public static Node insertMiddle(Node head, Node newNode, int position) {
Node cur = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 新节点的next指向cur的next的节点
newNode.next = cur.next;
// cur的下一个节点的prev指针指向newNode
cur.next.prev = newNode;
// 新节点的prev指向cur
newNode.prev = cur;
// cur的next指向新节点
cur.next = newNode;
return head;
}尾部
相对就简单了,只需要遍历到最后一个不为null的节点,将newNode节点接入最后一个节点就可以了
public static Node insertTail(Node head, Node newNode) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
newNode.next = null;
return head;
}总结
步骤:
- 判断原链表是否为空,为空直接返回新链表
- 判断位置是否在范围内,不在就返回
- 如果位置是1,也就是头插法
- 其他是中部和尾部方法,找到对应目标的前一个节点,然后就是中部插入的方法
public static Node insertNode(Node head, Node newNode, int position) {
// 1. 判断是否为空
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
// 计算长度
int length = getLength(head);
//2.位置是否合理
if(position<1 || position>length+1){
System.out.println("位置不合理");
return head;
}
//3. 头插法
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
// 4. 找到前一个节点
int count = 1;
Node cur = head;
while (count < position - 1) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 开始插入
newNode.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = newNode;
}
newNode.prev = cur;
cur.next = newNode;
return head;
}删除元素
单链表
头删
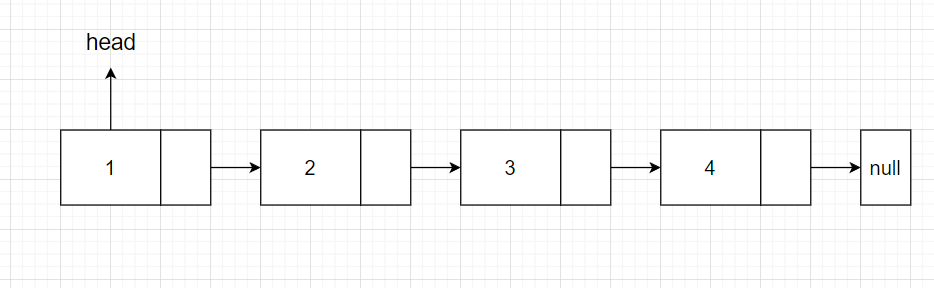
相对简单,只需要执行head = head.next,然后jvm会来执行对应的垃圾回收
指定位置删除
比如我现在想删除第三个节点也就是3
步骤:
- 先找到第二个节点的位置
- 然后将第二个节点的next指向第三个节点的next,也就是第四个节点
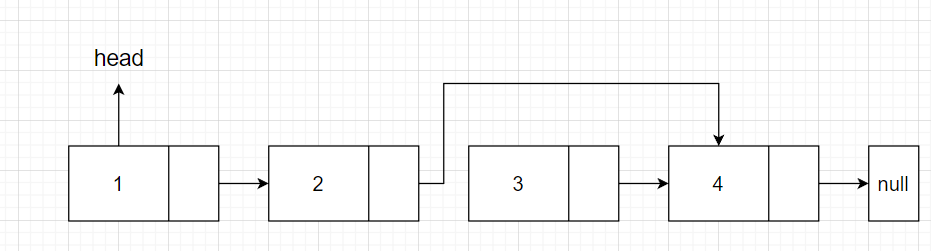
cur.next = cur.next.next尾部删除
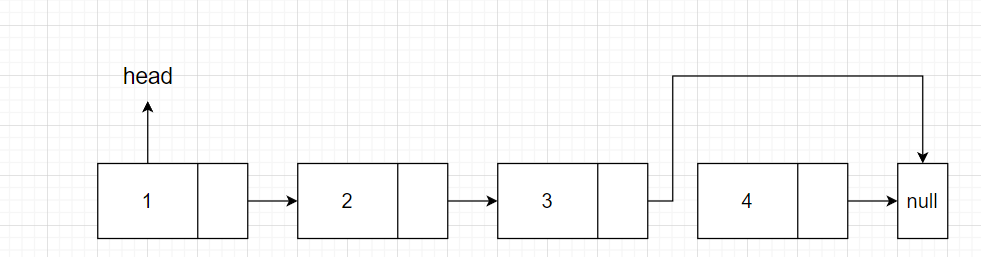
也是同理,不过只需要获取最后一个节点的前一个节点,然后这个节点指向null就可以了
总结
步骤:
- 判断是否为空,为空删除失败
- 不为空,判断删除位置是否合理
- 删除位置为1,表示头节点,直接删
- 删除其他位置,遍历到指定位置的前一个节点位置操作。
/**
* 删除指定位置的节点
* @param head 头节点
* @param position 从1开始
* @return
*/
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
// 空链表,无法删除
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,无法删除");
return null;
}
int length = getListLength(head);
// 删除位置不合法
if (position < 1 || position > length ) {
System.out.println("删除位置不合法");
return head;
}
// 头删除
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
// 删除指定位置
int count = 1;
Node cur = head;
while (count < position - 1) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return head;
}position > length 而不是`position > length +1,当输入的位置是最后一个节点的后面,也就是null,这时候如果加上了1,就认为这个null是一个节点,但是很显然,这个已经超出了这个长度,不合理。
双链表
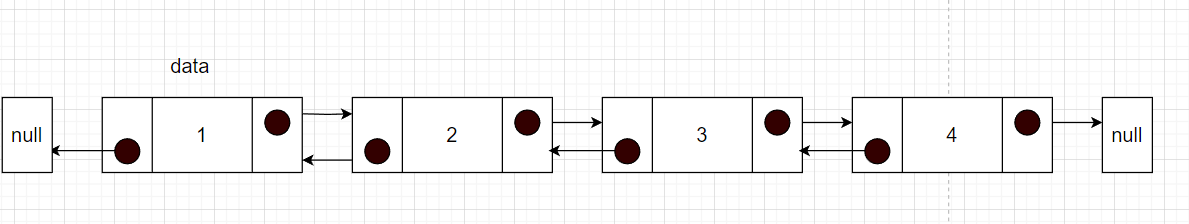
删除头节点
只需要将head移动到下面一个节点,然后让这个节点的prev指向null就可以
public static Node deleteHead(Node head) {
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return head;
}这边省去了判断head后面是否为空的步骤
删除中间指定位置
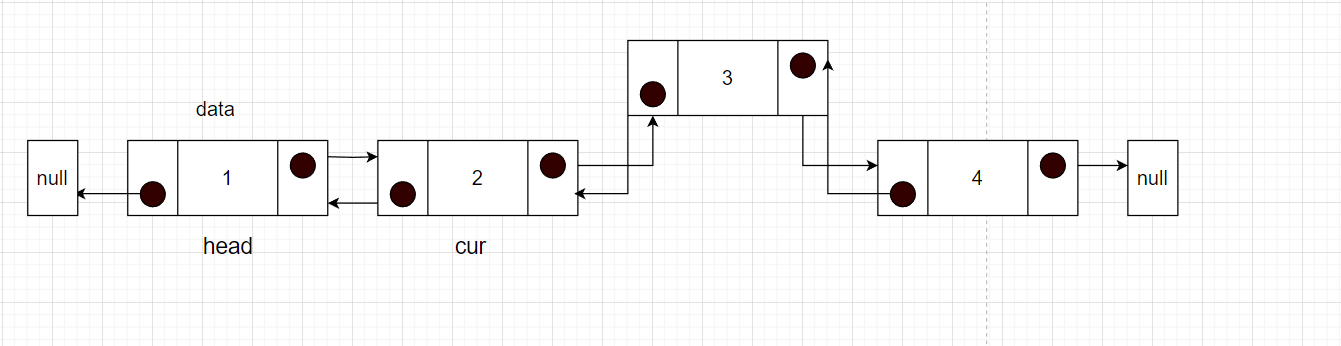
比如删除指定节点3
步骤:
- 找到删除指定位置的前一个节点cur
- 然后cur的next指向删除节点的下一个节点
- 然后这个节点再指向cur
public static Node deleteMiddle(Node head, int position) {
int count = 1;
Node cur = head;
while (count < position-1){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.prev = cur;
return head;
}其中设置postion-1的目的是找到前一个节点的位置,如果是position,当经过while条件的时候,此时cur是前一个节点,但是此时还是会找下一个next,那么此时就变成了指定节点的位置,而不是前一个节点了。
尾部删除
需要找到倒数第二个节点的位置,然后这个节点的next指向null
public static Node deleteTail(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
return head;
}这边省去了cur的next节点为空的情况
总结
步骤:
- 判断是否存在链表
- 判断删除位置是否合法
- 如果位置是1,头删法
- 其他方式需要取到删除节点的前一个节点的位置,需要判断两个节点是否为空
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("删除失败,不存在节点");
return null;
}
int length = getLength(head);
// 位置不合法
if (position < 1 || position > length) {
System.out.println("删除失败,位置不合法");
return null;
}
// 删除头节点
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
return head;
}
// 删除其他节点
int count = 1;
Node cur = head;
while (count < position - 1 && cur.next != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 判断下一个节点是否为空
if (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.prev = cur;
}
cur.next = null;
return head;
}这个里面删除的时候需要判断一些情况
- head的下一个节点为空
- 删除指定节点的时候,这个节点是空
- 删除指定节点的时候,这个节点的前一个节点也是空
时间复杂度
访问 O(n)
查找 O(n)
插入 O(1):插入指定位置节点的这个过程是O(n),只是这个插入操作时O(1)
删除 O(1):删除指定位置节点的这个过程是O(n),只是这个删除操作是O(1)
LinkedList源码分析
常见面试题
- 描述链表的数据结构?
- Java里面的LinkedList使用的是什么链表?
- 链表删除,插入,获取元素的时间复杂度是多少?
- 什么场景下使用链表比较合适?
leetcode算法
详情访问算法链表章节
贡献者
flycodeu
版权所有
版权归属:flycodeu
